NEW SYLLABUS OF CBSE SCHOOLS
CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 for 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th: Subject-wise New CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 (PDF) or CBSE Curriculum 2021-22 for 9th, 10th, 11th & 12th has been officially released online at cbseacademic.nic.in. The new CBSE Syllabus is applicable for CBSE Academic Session 2021-22. The board has already instructed CBSE Schools to start new CBSE Academic Session 2021-22 from April and the board has released the new syllabus before April 2021. There is no reduction in CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 for 9th, 10th, 11th & 12th.
As this CBSE Syllabus is applicable for Academic Session 2021-22, so students preparing for CBSE board exams 2021 has nothing to do with this syllabus. They can access their syllabus from this link.
CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 (PDF): Class 9
With the links given above, students of CBSE Class 9th can check & download the latest CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 (PDF).
CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 (PDF): Class 10
With the links given above, students of CBSE Class 10th can check & download the latest CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 (PDF).
CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 for Class 11
With the links given above, students of CBSE Class 11th can check & download the latest CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 (PDF).
CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 for Class 12
Chapter1
Access Answers of NCERT class 10 Science Chapter 1 – Chemical reactions and equations
In-text questions set 1 Page number – 6
1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Solution:
Magnesium ribbon should be cleaned before burning in air because Magnesium metal reacts with the atmospheric oxygen and forms Magnesium Oxide (MgO) layer which is a very stable compound. In order to prevent further reactions with Oxygen, it is therefore necessary to clean the ribbon by to remove the layer of MgO.
2. Write a balanced equation for the following chemical reactions.
i) Hydrogen + Chloride —-> Hydrogen chloride
ii) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate —-> Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
iii) Sodium + Water —-> Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Solution:
i) H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
ii) 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 →3BaSO4 + 2AlCl3
iii) 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
3. Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions
i) Solutions of Barium chloride and Sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble Barium sulphate and solution of Sodium chloride.
ii) Sodium hydroxide solution in water reacts with hydrochloric acid solution to produce Sodium chloride solution and water.
Solution:
i) BaCl2 + Na2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2NaCl
ii) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
In-text questions set 2 Page number – 10
1. A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for whitewashing.
(i) Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
(ii) Write the reaction of the substance ‘X’ named in (i) above with water.
Solution:
i) The substance ‘X’ which is used in whitewashing is quick lime or Calcium Oxide and its formula is CaO.
ii) CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
2. Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes in Activity 1.7 double of the amount collected in the other? Name this gas
Solution:
In activity 1.7, gas collected in one of the test tubes is double of the amount collected in the other because water gets hydrolysed to release H2 and O2 gas. Here, after electrolysis two molecules of Hydrogen and one molecule of oxygen gas is released, hence the amount of Hydrogen collected would be double than that of oxygen.
In-text questions set 3 Page number – 13
1. Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Solution:
When an iron nail dipped in the copper sulphate solution, iron displaces copper from the copper sulphate because iron is more reactive than copper. Therefore the colour of the copper sulphate solution changes. The reaction is:
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
2. Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in Activity 1.10.
Solution:
Reaction Between silver nitrate (AgNO3) and Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an example of double displacement reaction. During the reaction negative and positive ions trade positions as a result in the formation of white silver chloride precipitate. The chemical reaction is given below.
Ag+ + NO3– + Na+ + Cl– → AgCl + Na+ + NO3–
3. Identify the substances that are oxidized and that are reduced in the following equation.
i) 4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
ii) CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(l)
Solution:
The Sodium (Na) in the first equation is getting oxidized with the addition of Oxygen (O2) and the Copper (Cu) in the second equation is reduced due to the addition of Hydrogen (H2)
Exercise Questions Page number – 14-16
1. Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
2PbO(s) + C(s) → 2Pb(s) + CO2(g)
(a) Lead is getting reduced
(b) Carbon Dioxide is getting oxidised
(c) Carbon is getting oxidised
(d) Lead oxide is getting reduced
(i) (a) and (b)
(ii) (a) and (c)
(iii) (a), (b) and (c)
(iv) all
Solution:
(i) (a) and (b)
Explanation: (a) because Oxygen is being removed and (b) because the removed oxygen from Lead is added to the elemental Carbon.
2. Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
The above reaction is an example of a
- Combination reaction.
- Double displacement reaction.
- Decomposition reaction.
- Displacement reaction.
Solution:
Answer is 4. Displacement reaction.
Explanation: The Oxygen from the Ferrous oxide is getting displaced to the Aluminium metal to form Aluminium Oxide. In this reaction Aluminum is more reactive metal than Fe. Therefore Al will displace Fe from its oxide. This type of chemical reactions in which one of the elements displace another is called displacement reaction. Here less reactive metal is displaced by more reactive metal. Since one-time displacement is occurring, therefore, it is called a single displacement reaction.
3. What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron fillings? Tick the correct answer.
- Hydrogen gas and Iron chloride are produced.
- Chlorine gas and Iron hydroxide are produced.
- No reaction takes place.
- Iron salt and water are produced.
Solution:
- Hydrogen gas and Iron chloride are produced.
Explanation: The Chlorine from Hydrogen chloride is displaced by the Iron fillings to undergo the following reaction.
2HCl + Fe → FeCl2 + H2
4. What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should a chemical equation be balanced?
Solution:
A balanced equation is the one in which number of different atoms on both the reactant and product sides are equal. Balancing chemical equation is necessary for the reaction should obey The Law of Conservation of energy. Balancing the chemical equation has no defined method and is purely a trial and error attempt.
5. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and balance them.
(a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
(b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give Aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
(d) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and Hydrogen gas.
Solution:
(a) Unbalanced: H2 + N2 → NH3
Balanced: 3H2 + N2 → 2NH3
(b) Unbalanced: H2S + O2 → H2O + SO2
Balanced: 2H2S + 3O2 → 2H2O + 2SO2
(c) Unbalanced:
BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → AlCl3 + BaSO4
Balanced: 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → 2AlCl3 + 3BaSO4
(d) Unbalanced: K + H2O → KOH + H2
Balanced: 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2
6. Balance the following chemical equations.
(a) HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
(b) NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + HCl
Solution:
(a) 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
(b) 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
7. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reactions.
Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide —-> Calcium carbonate + Water
Zinc + Silver nitrate —-> Zinc nitrate + Silver
Aluminium + Copper chloride —-> Aluminium chloride + Copper
Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate —-> Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
Solution:
2Ca(OH)2 + 2CO2 → 2CaCO3 + 2H2O
Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
2Al + 3CuCl2 → 2AlCl3 + 3Cu
BaCl2 + K2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2KCl
8. Write a balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction of each case
KBr + BaI2 → KI + BaBr2
ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2
H2 + Cl → HCl
Mg + HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Solution:
2KBr + BaI2 → 2KI + BaBr2 (Double Displacement Reaction)
ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2 (Decomposition Reaction)
H2 + Cl → 2HCl (Combination Reaction)
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2 (Displacement Reaction)
9. What is meant by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Solution:
An endothermic reaction occurs when energy is absorbed from the surroundings in the form of heat.(Example: Photosynthesis, melting of ice, evaporation). Conversely, an exothermic reaction is one in which energy is released from the system into the surroundings. (Example: Explosions, concrete setting, nuclear fission and fusion).
10. Why is respiration considered to be an exothermic reaction?
Solution:
For the survival of life, we require energy. We obtain this energy from the food we eat. The food molecules, through the process of digestion, is broken down into a simpler molecule like glucose. These substances come in contact with the Oxygen present in our body cells to form Carbon dioxide and water along with a certain amount of energy (Respiration process). Since the energy is in the form of heat (that maintains our body temperature) the respiration is considered to be an exothermic reaction. The reaction taking place is:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
11. Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of Combination reactions? Write equations for decomposition reactions.
Solution:
Combination reaction is said to be the reaction between two or more molecules to form a larger molecule; whereas the decomposition reaction is defined as the splitting of larger molecules into two or more smaller molecules. This essentially explains that the decomposition reaction is the opposite of the combination reaction.
In most of the cases the decomposition reaction is endothermic since heat from the surrounding or induced heat is used to break the bonds of the larger molecule. Few examples of decomposition reactions are:
ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2
CaCO3 + Energy → CaO + CO2
2HgO → 2Hg + O2
12. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions in which energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Solution:
(a) Thermal decomposition reaction (Thermolysis)
Decomposition of potassium chlorate: When heated strongly, potassium chlorate decomposes into potassium chloride and oxygen. This reaction is used for the preparation of oxygen.
2KClO3 + Heat → 2KCl + 3O2
(b) Electrolytic decomposition reaction (Electrolysis)
Decomposition of sodium chloride: On passing electricity through molten sodium chloride, it decomposes into sodium and chlorine.
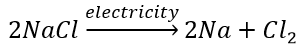
(c) Photodecomposition reaction (Photolysis)
Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide: In the presence of light, hydrogen peroxide decomposes into water and oxygen.
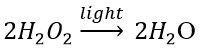
13. What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write relevant equations for the above.
Solution:
A displacement reaction is the one when a more reactive substance displaces a less reactive one from its salt solution whereas a double displacement reaction is the one where a mutual exchange of ions happens between two compounds.
In a displacement reaction, only a single displacement takes place whereas in the double displacement reaction, as the name suggests two displacement takes place between the molecules.
Example:
Displacement reaction
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Double displacement reaction
2KBr + BaI2 → 2KI + BaBr2
14. In the refining of Silver, the recovery of silver from Silver nitrate solution involves displacement reaction by Copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Solution:
Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
15. What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples.
Solution:
When two solutions containing soluble salts are combined, a double displacement reaction takes place in which the ions are exchanged between the compounds. When one of such compounds formed is in solid form (that is insoluble in aqua) then it settles down at the bottom of the container. This solid is known as the precipitate and the respective reaction is termed as the precipitation reaction. Few examples of precipitation reactions are:
CdSO4(aq) + K2S(aq) → CdS(s) + K2SO4(aq)
2NaOH(aq) + MgCl2(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + Mg(OH)2(s)
16. Explain the following in terms of gain of oxygen with two examples each.
(a) Oxidation
(b) Reduction
Solution:
(a) In a chemical reaction, when the oxygen is added to the element to form its respective oxide it is the element being oxidised. Example:
4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
H2S + O2 → H2O + SO2
(b) In a chemical reaction, when the oxygen is being removed from the compound then it is said to be reduced. Example:
CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(l)
2HgO → 2Hg + O2
17. A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in the air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Solution:
The shiny brown coloured element is the Copper metal (Cu). When the metal is heated in air, it reacts with atmospheric oxygen to form copper oxide. Hence, the black coloured compound is the copper oxide.
2Cu(s) + O2(g) → 2CuO(s)
18) Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Solution:
Iron articles are painted to prevent them from rusting. When left unpainted, the metal surface comes in contact with the atmospheric oxygen and in the presence of moisture it from Iron(III) oxide. But if painted the surface does not come in contact with moisture and air thus preventing Rusting.
19) Oil and Fat containing food items are flushed with Nitrogen. Why?
Solution:
The main purpose of flushing Nitrogen into food packets that contain oil and fat items is to prevent Rancidity which occurs when the oil or fat reacts with the oxygen letting out an unpleasant smell and taste. Therefore, by flushing Nitrogen, an unreactive surrounding is created thus preventing rancidity.
20) Explain the following terms with one example each.
(a) Corrosion
(b) Rancidity
Solution:
(a) Corrosion is a process where a refined metal is oxidised by atmospheric oxygen to form a more stable compound such as oxides. The metal gradually degrades during the corrosion process. Rusting of iron is a good example of corrosion where the iron is converted to Iron oxide. Millions of dollars are spent annually in preventing rusting from bridges and other monuments.
(b) The condition produced by the aerial oxidation of the oil and fat present in the food material that produces an unpleasant taste and smell. The rancidity is retarded when the food is kept inside the refrigerator since the low temperature does not promote the oxidation reaction.
Chapter2
In-text questions set 1 —> Page number 18
1. You are given three test tubes. The three test tubes contain distilled water, acidic solution and the basic solution respectively. There is only red litmus paper available in order to identify what is there in each test tube. How will you find out what is in each of the test tubes?
Solution: We can identify the content in each of the test tubes using red litmus paper. This can be done by noticing the colour change of the red litmus paper.
- On litmus paper, the three solutions in the test tubes are poured separately.
- The solution which turns red litmus to blue contains a basic solution.
- Divide the formed blue litmus paper into two parts.
- The solution from the test tube which turns blue litmus paper to red will be the acidic solution.
- Solution of the test tube which do not change either red or blue litmus paper contain water.
NOTE: After immediate distillation, distilled water has a pH of 7. However, just within a few hours after distillation, it absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and turns slightly acidic with a pH of 5.8.
In-text questions set 2 —> Page number 22
1. Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
Solution: Curd and sour food substances contain acids; these acidic substances combine with metal. This reaction turns food to poison which damage people’s health.
2. Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas?
Solution: When an acid reacts with any metal, salt and hydrogen gas are formed.
Metal + Acid → Salt + Hydrogen gas
3. Metal compound A reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Solution: As metal compound released is Calcium Chloride the gas evolved here is CO2. Hence metal A should be Calcium Carbonate. Hence the reaction between Calcium Carbonate and HCl is
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (Aq) → CaCl2( Aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
in text questions set 3 Page number – 25
1. Why do HCl, HNO3, etc., show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
Solution: Release of H+ ion in water will make a compound acidic or non-acidic. Acids are the substance which upon dissociating with water results in production of Hydrogen ions. Some compounds show acidic character as they dissociate in the aqueous solution which results in the production of hydrogen ions (acids like HCl, HNO3).
Compounds similar to glucose or alcohol do contain hydrogen element but they do not show signs of acidic nature. The fact that the hydrogen in them will not separate as like the hydrogen in the acids. They will not separate to become hydrogen ions, on dissolving in the water.
2. Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity?
Solution: Charged particles are responsible for the conductance of electricity in an acid. These charged particles called as ions are the reason behind conductance of electricity in acid.
3. Why does dry HCl gas not change the colour of the dry litmus paper?
Solution: HCl does not give out Hydrogen ions, therefore HCl does not show any acidic behaviour and colour of the litmus paper remain the same on reacting with HCl gas.
4. While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Solution: While diluting an acid, it is recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid because if water is added to concentrated acid, it release huge amount of heat which may result in explosion and can cause acid burns on face, clothes and body parts. Hence it is safe to add acid to water but not water to acid.
5. How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affected when a solution of an acid is diluted?
Solution: When acid is added to water there will be a fixed amount of hydronium present in the fixed volume of solution. If we dilute the solution hydronium ion per volume of solution decrease, this in-turn decreases Hydronium concentration in the solution.
6. How is the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide?
Solution: When base is dissolved in sodium hydroxide solution its hydroxide ions increase but it will reach saturation at some point. After saturation point hydroxide ion concentration is not affected even after adding base further.
In-text questions set 4 Page number – 33
1. You have two solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6 and pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of this is acidic and which one is basic?
Solution: In order to find the hydrogen ion concentration, we can use the rule that states, “The pH of any solution is inversely proportional to the hydrogen ion concentration”. Therefore, it means that the solution that has a lower pH number will have a higher hydrogen ion concentration. Hence, solution A will have a higher hydrogen ion concentration. In addition, solution B will be basic and A will be acidic.
2. What effect does the concentration of H+(aq) ions have on the nature of the solution?
Solution: Hydrogen ion concentration decides the nature of the solution. If Hydrogen ion concentration increase then solution turn acidic and similarly if Hydrogen ion concentration decreases then solution turn basic.
3. Do basic solutions also have H+(aq) ions? If yes, then why are these basic?
Solution: Basic solutions has H+ ions, but hydroxide ions present in basic solution are more in basic solution. Hence Hydroxide ions turn solution to basic.
4. Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate)?
Solution: If the soil is acidic in nature (PH below 7) then such field should be treated with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate).
In text questions set 5 Page number – 34-35
1. What is the common name of the compound CaOCl2?
Solution: Common name of CaOCl2 is bleaching powder.
2. Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder
Solution: The substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder is Calcium hydroxide.
3. Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Solution: Sodium carbonate is the compound which is used for softening hard water.
4. What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrocarbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Solution: Heating sodium hydrocarbonate yields sodium carbonate and carbon dioxide gas is liberated in the process.
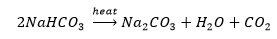
5. Write an equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Solution: The chemical equation for the reaction of Plaster of Paris and water is
CaSO4.1/2H2O + 3/2H2O → CaSO4.2H2O
Exercise questions Page number – 33
1. A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be
a) 1 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 10
Solution: Answer is 10 because litmus paper turns blue when reacts with basic solution (PH more than 7). Hence 10 is the answer.
2. A solution reacts with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime-water milky. The solution contains
a) NaCl (b) HCl (c) LiCl (d) KCl
Solution: Answer is HCl.
Egg shells contains calcium carbonate, which on reaction with HCl liberates CO2 gas which turn lime water to milky.
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
3. 10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 mL of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the amount HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be
(a) 4 mL (b) 8 mL (c) 12 mL (d) 16 mL
Solution: Since 10 ml of NaOH requires 8 mL of HCL, 20 ml of NaOH require 8 x 2 = 16mL of HCl. Hence the answer is option d 16mL.
4. Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion?
(a) Antibiotic (b) Analgesic (c) Antacid (d) Antiseptic
Solution: Indigestion is due to excess production of acid in the stomach. Medicines used to treat indigestion is called as Antacid.
5. Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
(b) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
(c) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(d) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
Solution:
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules:
=> dilute sulphuric acid + zinc → Zinc Sulphate + Hydrogen Gas
=> H2SO4(aq) + Zn → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
=> dilute Hydrochloric + Magnesium → Magnesium Chloride + Hydrogen Gas
=> 2HCl(aq) + Mg → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
=> dilute Sulphuric Acid + Aluminium → Aluminium Sulphate + Hydrogen Gas
=> 3H2SO4(aq) + 2Al(s) → Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g)
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
=> dilute Hydrochloric Acid + Iron → Ferrous Chloride + Hydrogen Gas
=> 6HCl(aq) + 3Fe(s) → 3FeCl2(aq) + 3H2(g)
6. Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an Activity to prove it
Solution: Insert two nails on the wooden or rubber cork and place them on a beaker as shown in figure. Connect iron nail to a bulb, 6 volt battery and a wire connected to switch. Pour some alcohol or glucose so as to dip the nails in glucose or alcohol. Turn the switch on and you the see the bulb not glowing despite of connection to switch. Now empty the beaker and add HCL solution. This time bulb glows. This proves acid can conduct electricity but alcohol and glucose does not conduct electricity.
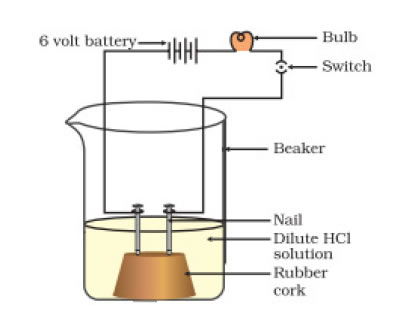
7. Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rain water does?
Solution:
- Distilled water does not contain any ionic compounds in it.
- Whereas rainwater has a lot, more compounds.
- Rainwater has dissolved acidic gas such as carbon dioxide from the air and that forms carbonic acid. This means that it has hydrogen ions and carbonate ions. Therefore, with the presence of acids, rainwater can conduct electricity.
8. Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Solution: The acidic behaviour from acids is because of the presence of hydrogen ions. Hydrogen ions can only be produced in the presence of water and therefore water is definitely needed if acids are to show their acidic behaviour.
9. Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9, respectively. Which solution is
(a) neutral?
(b) Strongly alkaline?
(c) Strongly acidic?
(d) Weakly acidic?
(e) Weakly alkaline?
Solution: In increasing order of hydrogen ion concentration:
pH 11(C) < pH 9(E) < pH 7 (D) < pH 4 (A) < pH 1 (B)
PH11 – Strongly alkaline
pH9 – weakly alkaline
PH7 – Neutral
pH4 – Weakly acidic
pH1 – Strongly acidic
10. Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube B. Amount and concentration taken for both the acids are same. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Solution: HCl is a strong acid whereas acetic is a weaker acid. Fizzing occurs because of the production of the hydrogen gas obtained due to reaction of the acid on the magnesium ribbon. Since HCl is a very strong acid there is a lot of liberation of hydrogen gas from test tube A. therefore, more fizzing take place in test tube A.
11. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Solution: Fresh milk is turned to curd due to production of lactic acid. Lactic acid reduces the pH of the milk.
12. A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
Solution: (a) He shifted the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline to prevent milk from getting sour due to production of lactic acid.
(b) This milk takes long time to set into curd because the lactic acid produced here first neutralises the pH then the pH is reduced to turn milk to curd.
13. Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
Solution: Plaster of Paris should be stored in moisture-proof container because moisture can affect plaster of Paris by slowing down the setting of the plaster because of hydration. This will turn plaster useless.
14. What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
Solution: The reaction of the acid + base gives a product of salt + water, which is considered as neutralization reaction.
Examples:
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
Mg(OH)2 + H2CO3 → MgCO3 + 2H2O
CHAPTER 3
In-text questions set 1 Page number 40
1. Give an example of a metal which
(i) Is a liquid at room temperature?
(ii) Can be easily cut with a knife?
(iii) Is the best conductor of heat?
(iv) Is a poor conductor of heat?
Solution:
(i) Mercury is the metal which is liquid at room temperature
(ii) Sodium and potassium are the metals which can be cut with a knife
(iii) Silver is the best conductor of heat
(iv) Mercury and lead are poor conductor of heat.
2. Explain the meanings of malleable and ductile.
Solution:
- Metals which can be beaten to sheets are said to be malleable
- Metals which can be drawn into thin wires are said to be ductile
In-text questions set 2 Page number 46
1. Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil?
Solution: Sodium is a reactive metals, if kept open it will react with oxygen to explore and catch fire. Sodium metal is kept immersed in kerosene to prevent their reaction with oxygen, moisture and carbon dioxide of air.
2. Write equations for the reactions of
(i) iron with steam
(ii) calcium and potassium with water
Solution: (i) Iron reacts with steam to form a magnetic oxide of Fe with the liberation of H2.
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
(ii) Calcium reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen.
Ca(s) + 2H2O(I) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
Potassium reacts with cold water violently immediately with evolution of H2 which catches fire.
2K(s) + 2H2O(I) → 2KOH(aq) + 2H2(g)
3. Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and added to the following solution one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows
| Metal | Iron(II) sulphate | Copper(II) sulphate | Zinc sulphate | Silver Nitrate |
| A | No reaction | Displacement | – | – |
| B | Displacement | – | – | – |
| C | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | Displacement |
| D | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
Use the Table above to answer the following questions about metals A, B, C and D.
- Which is the most reactive metal?
- What would you observe if B is added to a solution of Copper (II) sulphate?
- Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Solution:
(i) Metal B is the most reactive as it gives displacement reaction with iron (II) sulphate.
(ii) When metal B is added to copper (II) sulphate solution, a displacement reaction will take place because of which the blue colour of copper (II) sulphate solution will fade and a red-brown deposit of copper will be formed on metal B.
(iii)Metal B is the most reactive because it displaces iron from its salt solution. Metal A is less reactive because it displaces copper from its salt solution. Metal C is still less reactive because it can displace only silver from its salt solution and metal D is the least reactive because it cannot displace any metal from its salt solution. Hence, the decreasing order of reactivity of the metals is B > A > C > D.
4. Which gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal? Write the chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4.
Solution: Hydrogen gas is liberated when dilute HCl is added to a reactive metal.
Fe(s) + H2SO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + H2(g)
5. What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate? Write the chemical reaction that takes place.
Solution: Zinc is more reactive (more electro positive) than iron. Therefore Zinc displaces Iron from its salt solution. The colour of ferrous sulphate is pale green, which turns colourless.
FeSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Fe(s)
Light green Zinc sulphate(Colourless)
In-text questions set 3 Page number 49
1. (i) Write the electron-dot structures for sodium and oxygen.
(ii) Show the formation of Na2O and MgO by the transfer of electrons.
(iii)What are the ions present in these compounds?
Solution: (i) Sodium:

Oxygen:

(ii) Formation of Magnesium oxide:
When magnesium reacts with oxygen, the magnesium atom transfers its two outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing two electrons, the magnesium atoms form a magnesium ion (Mg2+) and by gaining two electrons, the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion (O2-).
Mg: + → MgO
→ MgO
Formation of Sodium oxide:
Two sodium atoms transfer their 2 outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing two electrons, the two sodium atoms form sodium ions (2Na+). And by gaining two electrons, the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion (O2-).
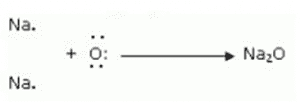
(iii) The ions present in sodium oxide compound (Na2O) are sodium ions (2Na+) and oxide ions (O2-).
The ions present in Magnesium oxide compound (MgO) are magnesium ions Mg2+ and oxide ions (O2-).
2. Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Solution: Ionic compounds are the ones which has both positive and negative charges. Hence there will be strong force of attraction between them. This make expenditure of lot of heat to break this force of attraction hence ionic compounds have high melting points.
In-text questions set 4 Page number 53
1. Define the following terms.
(i) Mineral
(ii) Ore
(iii) Gangue
Solution:
- Minerals are compounds (also known as elements) which are found naturally in the earth’s crust. E.g. Alums, K2SO4.Al2(SO4)3.24H2O, etc.
- Ores are minerals from which metal can be extracted Ex: Bauxite Al2O3.2H2O is the ore of Al, copper pyrite CuFeS2.All minerals are not considered as ores but all ores are also minerals.
- Ores mined from the earth are naturally contaminated with sand, rocky materials. There are impurities present in the ore which are known as gangue.
2. Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state
Solution: Gold and platinum are the two metals found in Free State in nature.
3. What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
Reduction method is used to obtain metal from its oxide. Ex: Zinc oxide is reduced to metallic zinc by Heating with carbon.
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
Ex: Lead oxide is reduced to lead by heating with carbon
PbO +C → Pb + CO
In-text questions set 5 Page number 55
1. Metallic oxides of zinc, magnesium and copper were heated with the following metals.
| Metal | Zinc | Magnesium | Copper |
| Zinc Oxide | |||
| Magnesium Oxide | |||
| Copper Oxide |
Solution:
A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its oxide. Among Zinc, Magnesium, and Copper metals, magnesium is the most reactive, copper is the least reactive metal and zinc is less reactive .The displacement reaction will take place in the following cases
| Metal | Zinc | Magnesium | Copper |
| Zinc Oxide | – | Displacement | – |
| Magnesium Oxide | – | – | – |
| Copper Oxide | Displacement | Displacement | – |
2. Which metals do not corrode easily?
Solution: Gold and platinum are the metals which do not corrode easily
3. What are alloys?
Solution: An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal.
Exercise questions Page number 56-57
1. Which of the following pairs will give displacement reactions?
(a) NaCl solution and copper metal
(b) MgCl2 solution and aluminium metal
(c) FeSO4 solution and silver metal
(d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal
Solution: Option d i.e AgNO3 solution and copper is correct answer. Copper displace the silver cations (reducing them to the elemental metal), in the process copper itself being oxidised to Copper II cations (Cu2+) and going into solution. So silver metal precipitating out and a copper II nitrate solution will be remaining.
Cu(s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) → Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag (s)
2. Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting?
- Applying grease
- Applying paint
- Applying a coating of zinc
- All of the above
Solution: Answer is (c) Applying a coat of Zinc
Though applying grease and applying paint prevents iron from rusting but we cannot apply these methods on frying pan hence applying a coat of Zinc is most appropriate method to prevent an iron pan from rusting.
3. An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. The element is likely to be
(a) Calcium
(b) Carbon
(c) Silicon
(d) Iron
Solution: Correct answer is option (a) i.e Calcium.
Calcium reacts with oxygen to give calcium oxide. Calcium oxide is soluble in water to give Calcium Hydroxide.
Carbon forms carbon-oxide with oxygen which is gas hence option B is wrong
Silicon reacts with oxygen and forms silicon dioxide. This is insoluble in water. So option C is not correct.
Iron reacts with oxygen and forms Iron dioxide. This is insoluble in water. So option D is not correct.
4. Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because
(a) Zinc is costlier than tin.
(b) Zinc has a higher melting point than tin.
(c) Zinc is more reactive than tin.
(d) Zinc is less reactive than tin.
Solution: Answer is c. Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because Zinc is more reactive that is electro positive than tin.
5. You are given a hammer, a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch.
(a) How could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non-metals?
(b) Assess the usefulness of these tests in distinguishing between metals and non-metals.
Solution:
- Metals are malleable and can be easily drown into sheets by hitting with hammer. On the other hand if we beat non-metals they break down and they cannot be drawn into sheets as they are non-malleable. Metals of good conductors of electricity hence they make bulb when you connect metals with a battery, wire and bulb. Similarly If non-metals are bad conductors of electricity chance they fail to lit up the bulb on connecting with wire and battery.
- These experiments can be helpful to demonstrate the malleability and electric conductivity of the metals and non-metals
6. What are amphoteric oxides? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides
Solution: Oxides that react with both acids and bases to form salt and water are known as amphoteric oxides. Examples: PbO and Al2O3.
Amphoteric oxides are the one which reacts with both acids and bases to form salt and water. Examples: Lead oxide – PbO and Aluminium oxide – Al2O3.
7. Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Solution: Zinc (Zn) and Magnesium (Mg) are the two metals which will displace Hydrogen from dilute acids as they are very reactive metals. Gold (Au) and Silver (Ag) are the metals which will not replace Hydrogen from dilute acids as these metals are less reactive.
8. In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Solution: In the process of electrolytic refining of metal called ‘M’, An impure and thick block of metal M. is considered as anode, Thin strip or wire of pure metal M is taken as cathode. A suitable salt solution of metal M is considered as the electrolyte.
9. Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test tube over it, as shown in figure below.
(a) What will be the action of gas on
(i) dry litmus paper?
(ii) moist litmus paper?
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
Solution: a) When sulphur powder is burnt in the air sulphur-di-oxide is formed.
(i) Sulphur-di-oxide does not have any effect on dry litmus paper.
(ii) Sulphur-di-oxide turn the moist litmus paper from blue to red as contact of SO2 with water turns to sulfurous acid.
(b) S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g)
SO2(g) + H2O →H2SO3
10. State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Solution:
- Iron can be prevented from rusting by coating the surface of the iron with rust proof paints
- By applying Oil/grease on the surface of iron objects as it will prevent the iron surface to get in contact with air consisting of moisture.
11. What type of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen?
Solution: When non-metals combine with oxygen it forms either acidic or neutral oxides. Ex: N2O5 or N2O3 is an acidic oxide; CO is a neutral oxide.
12. Give reasons
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
(d) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction
Solution:
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery for these metals are very less reactive hence they are not affected by air, water or most chemicals. These metals have a lot of luster and they are malleable and ductile in nature and also high corrosion resistance in nature.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium readily react with water to produce a lot of heat. As a result, Hydrogen evolved in the reaction results in a fire. On exposure to water they react with moisture (water droplets) present in the atmosphere, In order to prevent contact with water hence these metals are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium forms on its surface a nonreactive surface of aluminium oxide. Such coating prevents other compounds from reacting to aluminium. So aluminium is being used to produce utensils for cooking.
(d) Reducing metal oxide into free metal is easy. Additionally, because it is easier to obtain metals directly from their oxides than from their carbonates or sulphides, the carbonate and sulphide ores are first transformed to oxides to obtain the metals.
13. You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels.
Solution: Tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind because this sour substance contains acids which dissolve the coating of copper oxide or basic copper carbonate present on the surface or tarnished copper vessels. This makes them shining red-brown again. Hence they are very effective in cleaning tarnished copper vessels.
14. Differentiate between metal and non-metal on the basis of their chemical properties.
Solution:
| Metals | Non-metals |
| When metals are heated with oxygen, they form ionic oxides which are basic in nature and form bases on dissolving with water. This turn red litmus paper to blue. | When non-Metals are heated with oxygen, they form covalent oxides which are acidic in nature which form acid on dissolving with water. This turn blue litmus paper to red. |
| They are electro positive, lose electrons readily and become a positive ion. | They are electro negative, gain electrons and become negative ions. |
| Metals are lustrous. | Non-metals are non-lustrous; graphite is the exception |
| Reducing agents. | Good oxidizing agents. |
| Metals are the good conductors of electricity and heat. | Non-metals are non-conductors of electricity and heat; graphite is the exception |
| All metals are solids except mercury. | Non-metals are in solid-liquid and gaseous states |
15. A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Solution: Goldsmith used the solution called Aqua regia which is called as royal water in Latin. It is the mixture of concentrated Hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid in the ratio of 3:1. Aqua regia is capable of dissolving noble metals like gold and platinum. When upper-layer of dull gold ornament is dissolved they lose their weight.
16. Give reasons why copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel (an alloy of iron).
Solution: Copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel (an alloy of iron) because copper does not reacts with either water or steam whereas iron reacts with steams to corrode the tank.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3- Metals and Non-metals
Elements can be categorised into two types viz, Non-Metals and Metals. Excluding mercury, all metals are solid at room temperature. Some other important properties of metals include
- They are malleable
- Lustrous
- Good conductors of electricity and heat
- They lose their electrons to form positively charged ions
- They form basic oxides by combining with oxygen
What are amphoteric oxides?
Oxides which show basic and acidic properties are called amphoteric oxides. Examples are, zinc oxide and aluminium oxide.
What is metallurgy?
The process of extracting metal from ore and refining it is called metallurgy.
What is corrosion?
Corrosion is a phenomenon where a metal like iron is exposed to moistened air for a long period.
What are non-metals?
Non-metals are not ductile and malleable. Excluding graphite, all non-metals are bad conductors of electricity and heat. They gain electrons to form negative ions when they react with metals. Non-metals form hydrides by reacting with hydrogen. They can form oxides which are either neutral or acidic.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 – Metals and Non-metals
- The information provided in these NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 – Metals and Non-metals is authentic and easy to understand.
- These solutions provide answers to all the exercise questions present at the end of Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals from NCERT Class 10 Science textbook.
- The solutions to questions asked in between the chapter have also been provided.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 – Metals and Non-metals are provided by BYJU’S subject experts only after extensive research.
- These solutions will be useful for various competitive exams such as JEE, NEET, etc.
- Students can rely on these solutions to prepare for their board exam as it consists of tips, shortcuts, step by step procedure and neat labelled diagrams to tackle the complex type of questions smartly.
To get NCERT Class 10 Chapter-wise solutions for other subjects, you can check out NCERT Solutions for Class 10.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3
List out the differences between metals and non metals based on their physical properties in Chapter 3 of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science.
1. All metals are solid at room temperature except mercury whereas the non-metals can be in solid, liquid or gas form.
2. Metals are lustrous whereas non metals are non lustrous.
3. Metals possess high density whereas non metals possess low density.
4. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity whereas non metals are poor conductors.
5. Metals have high melting point whereas non metals have low melting and boiling point.
Mention the uses of metals and non metals explained in the Chapter 3 of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science.
CHAPTER 4
(All In text and Exercise Questions Solved)
In-text questions set 1 Page number 61
1. What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2?
Solution:
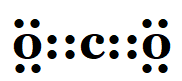
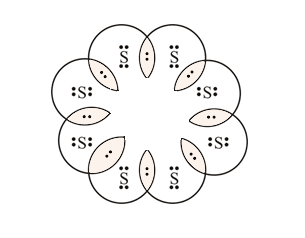
2. What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of Sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of Sulphur? (Hint – The eight atoms of Sulphur are joined together in the form of a ring).
Solution:
In-text questions set 2 Page number 61
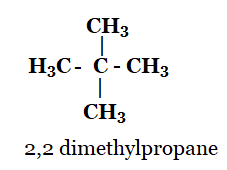
1. How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Solution: Structural isomer of pentane are
n-pentane
2-methylbutane
2, 2-dimethylpropane
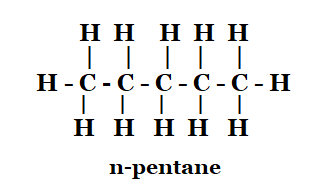
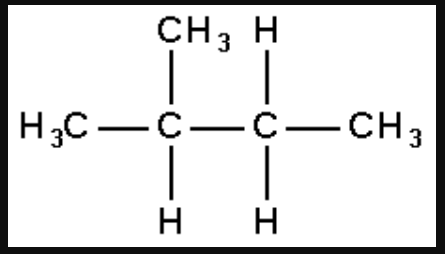
2-methylbutane
2. What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Solution: Two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us are
- Carbon has six valence electrons which are actually a high number of valency.
- Covalent bonding happens easily with carbon atoms and numerous others such as oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen, Sulphur, hydrogen, etc.
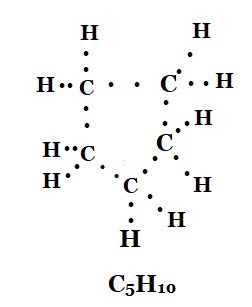
3. What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane?
Solution:
4. Draw the structures for the following compounds.
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Bromopentane*
(iii) Butanone
(iv) Hexanal
Solution: i)
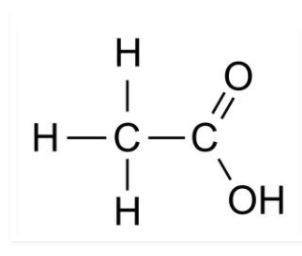
ii)
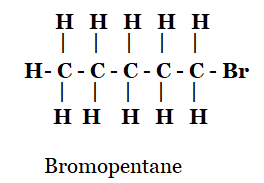
iii)
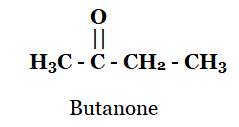
iv)
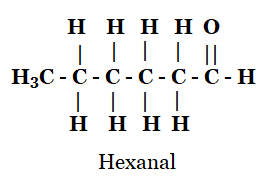
5. How would you name the following compounds?
- CH3—CH2—Br
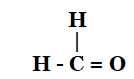
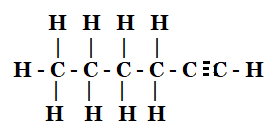
Solution:
- Bromoethane
- Methanal or Formaldehyde
- 1 – Hexyne
In-text questions set 3 Page number 71
1. Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction?
Solution:
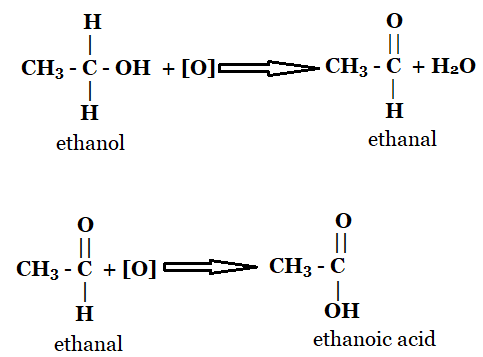
Conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid involves the removal of Hydrogen atom and addition of oxygen it is an oxidation reaction. In the first step, a H2 molecule is removed from ethanol to form ethanal. As loss of Hydrogen is oxidation so, the reaction is an oxidation reaction. Similarly Oxygen atom is added to form ethanoic acid from ethanal. As, gain of Oxygen is called oxidation so, the reaction is an oxidation reaction.
2. A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Solution: A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding instead of mixture of ethyne and air because the production of heat is very important for welding metals. When oxygen and ethyne are burnt, it burns completely and produces a higher temperature than air and ethyne. Oxygen and ethyne produce very hot blue flame but the mixture of air and ethyne gives out a sooty flame which means that there are unburnt particles, resulting in lesser heat.
In text questions set 4 Page number 74
1. How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid?
Solution: On reaction with Sodium Carbonate, Carboxylic acids produces carbon dioxide gas which turns lime water milky whereas alcohols do not give this reaction. This experiment can be used to distinguish an alcohol and carboxylic acid.
Reaction of Carboxylic acid with sodium carbonate:
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
2. What are oxidising agents?
Solution: Oxidising agents are those compounds which either removes Hydrogen or adds oxygen to a compound. Ex: halogens, potassium nitrate, and nitric acid.
In text questions set 5 Page number 76
1. Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent?
Solution: It is not possible to check if water is hard by using a detergent because detergents are salts of ammonium or sulphonates of long chain carboxylic acids. Unlike soaps they do not react with calcium and magnesium to distinguish nature of water.
2. People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes?
Solution: Agitation is necessary to get clean clothes as agitation aid soap micelles to trap the oil, grease or any other impurities that have to be removed. When they are being beaten or agitated, the particles are removed from the clothes’ surfaces and go into the water, thus cleaning the clothes.
Exercise questions Page number 77-78
1. Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has
(a) 6 covalent bonds.
(b) 7 covalent bonds.
(c) 8 covalent bonds.
(d) 9 covalent bonds
Solution: Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has 7 covalent bonds
2. Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) alcohol
Solution: Answer is option C i.e Ketone.
3. While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(a) the food is not cooked completely.
(b) the fuel is not burning completely.
(c) the fuel is wet.
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
Solution: Answer is option b. While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside indicates that the fuel is not burning completely.
4. Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl
Solution: Carbon can neither lose 4 electrons nor do gain four electrons as these process make the system unstable due to requirement of extra energy. Therefore CH3Cl completes its octet configuration by sharing its 4 electrons with carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements. Hence the bonding that exists in CH3Cl is a covalent bonding.
Here, carbon requires 4 electrons to complete its octet, while each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete its duplet. Also, chlorine requires an electron to complete the octet. Therefore, all of these share the electrons and as a result, carbon forms 3 bonds with hydrogen and one with chlorine.
5. Draw the electron dot structures for
(a) ethanoic acid
(b) H2 S
(c) propanone
(d) F2
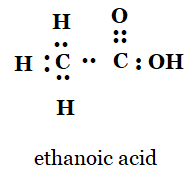
Solution:
a)
b)
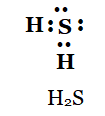
c)
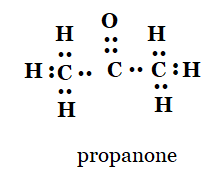
d)
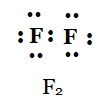
6. What is a homologous series? Explain with an example.
A homologous series is a series of compounds, which has the same functional group. This also contains similar general formula and chemical properties. Since there is a change in the physical properties, we can say that there would be an increase in the molecular size and mass.
For example, methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc. are all part of the alkane homologous series. The general formula of this series is CnH2n+2. Methane CH4 Ethane CH3CH3 Propane CH3CH2CH3 Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3. It can be noticed that there is a difference of −CH2 unit between each successive compound.
7. How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
Solution:
| Ethanol | Ethanoic acid |
| Does not react with sodium hydrogen carbonate | Bubbles and fizzes with sodium hydrogen carbonate |
| A good smell | Smells like vinegar |
| No action in litmus paper | Blue litmus paper to red |
| Burning taste | Sour taste |
8. Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also?
Solution: Micelle formation takes place because of the dirt particles in water and clean water. There are two mediums that are involved: one is pure water and the other being dirt (also called as impurities). The soap also has two mediums:
(i) organic tail and
(ii) ionic head
So the organic tail mixes and dissolves with the dirt whereas the oil or grease and ionic head dissolves and mixes with the water. Therefore, when the material to be cleaned is removed from the water, the dirt is taken off by the soap molecules in the water. Hence, the soap cleans by forming closed structures by the mutual repulsion of the micelles (positively charged heads).
Other solvents such as ethanol, in which sodium salt of fatty acids does not dissolve, so not able to form such micelles.
9. Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Solution: Carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications for they have high calorific values and give out a lot of energy. Most of the carbon compounds give a lot of heat and light when burnt in air.
10. Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap?
Solution: Scrum is produced from reaction of hard water with soap. Calcium and magnesium present in the hard water form an insoluble precipitate that stick as a white which is also called as scrum.
11. What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Solution:When soap is dissolved in water, due to the formation of alkaline NaOH or KOH, the solution is alkaline. The solution changes the colour of the red litmus to blue, but in the soap solution, the blue litmus remains blue.
12. What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Solution: Hydrogenation is a process or a chemical reaction between hydrogen and other compounds. It is usually done in the presence of catalysts: for example nickel, palladium or platinum. Hydrogenation is used mainly to saturate organic compounds.
13. Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions: C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4.
Solution: Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions. C3H6 and C2H2 are unsaturated hydrocarbons which undergo addition reactions.
14. Give a test that can be used to differentiate between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Solution: Bromine water test – is used to differentiate between the unsaturated compounds (like alkenes and alkynes) and the saturated compounds. For this purpose, bromine is used in the form of bromine water. A solution of bromine in water is called bromine water. Bromine water has a red-brown color due to the presence of bromine in it. When bromine water is added to an unsaturated compound, then bromine gets added to the unsaturated compound and the red-brown color of bromine water is discharged. So, if an organic compound decolorizes bromine water, then it will be an unsaturated hydrocarbon (containing a double bond or a triple bond), but saturated hydrocarbon (alkanes) do not decolorize bromine water.
Bromine water test is perform to differentiate between the unsaturated compounds (like alkenes and alkynes) and the saturated compounds. Bromine water is added to an un-saturated hydrocarbon red brown color of bromine solution is discharged. So if there is dis-coloration then the compound will be an unsaturated Hydrocarbon.
15. Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Solution: There are so many impurities and dirt mixed in water, and most of all the dirt does not dissolve in the water. Soap molecules are a combination of salts such as sodium or potassium. The molecules are of a long chain of carboxylic acids. So, when the carbon chain is dissolved in oil and the ionic end is dissolved in the water, the soap starts cleansing and trapping the dirt. When this happens, the soap molecules form structures that are called micelles are used for capturing the oil droplets and then the other end being the ionic faces. This will then form an emulsion in water and help in dissolving the dirt or impurities when the clothes are washed.
The soap molecules have different properties at different ends. The first end being the hydrophilic end which dissolves in the water and is attracted towards the water and the second one being the hydrophobic end is dissolved in the hydrocarbons and is repulsive to water. The hydrophobic tail aligns itself along the surface of the water because it is not soluble in the water.








0 Comments